OGC Member Intel recently launched Intel Geospatial, a cloud-based geospatial data management, visualization, and AI platform with applications in asset management across utilities smart cities, energy, and other industries. Launched in partnership with other geospatial and IT companies, the platform features a range of multi-source data types, geovisual data management, 3D visualization, analytic applications, and enterprise integration capabilities. Crucially, the platform supports a variety of OGC standards including 3D Tiles, WMS, WMTS, CDB, CityGML, GeoTiff, LAS, KML and others, enabling seamless interoperability with other OGC compliant systems and data sources.
“Across its traditional businesses, Intel has always been a big proponent of open standards,’ said Vijay Krishnan, General Manager, Intel Geospatial. “At Intel Geospatial, we are practicing this principle from our inception. Our use of open standards can help customers solve new use cases by taking advantage of AI model development from Intel, our partners, and their own data science teams through an open ‘plug-in’ architecture. We believe our platform creates value by fostering interoperability and reuse, and by giving end-users more choice.”
Indeed, open standards, such as those from OGC, have enabled the creation of innovative data integration solutions, such as Intel Geospatial, that take advantage of the abundant geospatial data now being created by countless different providers.
“Over the last decade, geospatial data has seen an explosion in terms of higher resolutions, increasing frequencies and greater coverage of the planet, aided by new innovations in terrestrial and aerial capture methods,” said Vijay. “This in turn has led to significant challenges in data management, visualization, and analysis. Fortunately, advances in cloud computing and artificial intelligence have made it possible for a new generation of software and services to deliver unprecedented scale, capabilities, ease-of-use, and interoperability.
“From our perspective, OGC has been instrumental in defining standards like WMS, WMTS, WFS, and 3D Tiles, which are critical to sharing and delivering geospatial information to create geo-enabled solutions. OGC has been the glue that brings industry players together to work for the common good of the industry and for greater end-user value.”
Intel recently became an OGC member in order to bring their broad expertise and interest to our collaborative standards development process.
“Looking at the rapidly evolving industry of AI and geospatial artificial intelligence (GeoAI), we believe that participating in the development and use of standards will help accelerate high-value AI-powered applications through collaborative AI development,” said Vijay.
“We are interested in several areas covered by the Domain Working Groups including Artificial Intelligence in Geoinformatics, Smart Cities, Built Environment and 3D, Security and Workflow DWGs. Being new to the OGC, we are in a learning phase with regards to OGC standards development with plans to increase our participation in areas where we have expertise and can provide value.”
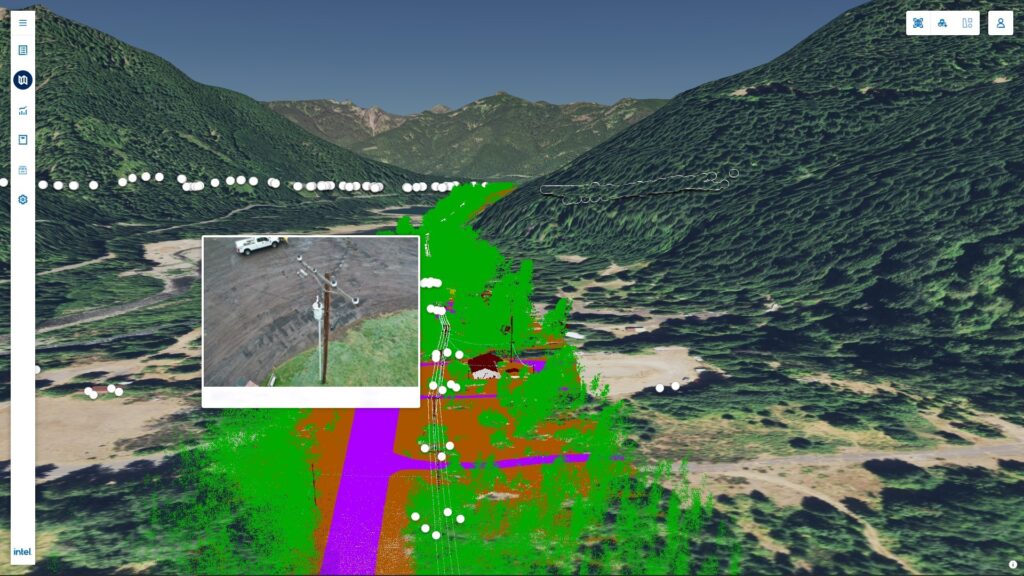
Indeed, the Intel Geospatial platform has applications across each of these domains: it runs on Intel’s datacenter and cloud technologies and integrates with AI to create workflows that use different sources of remote-sensed imagery to provide insights on assets across a number of applications.
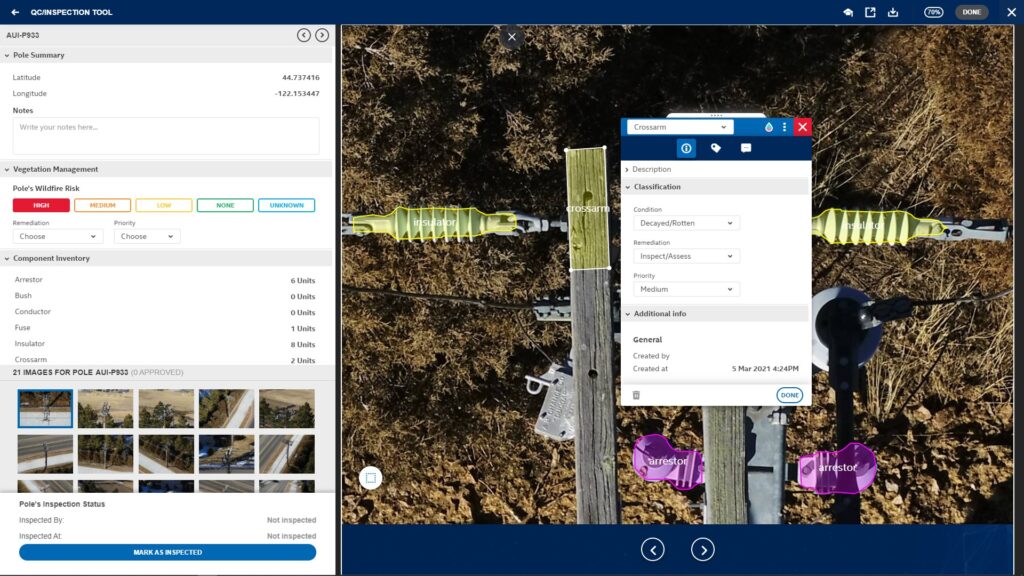
“Despite being a relatively new offering, we have been very fortunate in working with partners and customers on projects across energy, utilities, smart cities, and insurance,” said Vijay. “Probably the biggest area of interest across these verticals is using geospatial data and artificial intelligence to conduct more frequent, comprehensive, and efficient asset assessment. The need to better identify, prioritize, and predict issues for intelligent asset management at scale is driving their move to more automated and analytics-based solutions.”
Intel believes that the coupling of AI with cloud technologies will play a critical role in the improvement of automation and analytics, and fuel tremendous growth.
“Industry analysts predict geospatial workloads will see a steady shift to the cloud,” said Vijay. “There is also rapid advancement of AI capabilities that will need to be harnessed across industries and organizations for end-user benefit. We believe these two trends are fundamental tenets that will fuel the next wave of growth in the geospatial industry.
“AI will have transformational impacts on the ways geospatial data will be processed and utilized. Advances in AI for LiDAR classification, feature extraction, and analysis will help solve one of the biggest challenges with LiDAR: the time between data collection and the delivery of actionable results.
“Capitalizing on this, Intel Geospatial is turning labor-intensive asset management into a streamlined, data-driven science, making it easier to extract business insights at scale.”
Using OGC standards, the Intel Geospatial platform is providing simple access to a wide range of high-quality 2D and 3D geospatial data and analytic applications for asset owners and service provider businesses that collect geospatial imagery using drones, planes, vehicles, and more. Supported current use cases include electrical infrastructure inspections and vegetation management, with bult-in extensibility to support future use cases via a ‘plug-in’ architecture. This growing ecosystem of plug-in analytics will help transform geospatial data into smarter, more efficient business solutions.
