Imagine a platform that maps every corner of a varied and vibrant country like India—a digital window that not only captures its sprawling landscapes but also powers solutions for its most pressing challenges. Enter Bhuvan, India’s very own geospatial powerhouse, developed by OGC Member National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), one of the primary centers of the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). Launched in 2009, Bhuvan is more than just maps and data; it is a tool of transformation. From empowering rural livelihoods to aiding disaster relief, Bhuvan weaves together technology, governance, and human effort to chart a brighter future for India. Enabled by OGC Standards, this platform is not just about visualizing the country—it is about reimagining it.
The Bhuvan web portal provides extensive and comprehensive access to satellite imagery and geospatial data covering the entire country. It supports applications that provide detailed geospatial analysis and mapping features, which in turn facilitate developmental planning, disaster management, inventory management, environmental conservation, and more. Aided by an intuitive interface, Bhuvan enables users to visualize, analyze, and share geospatial information. Users range from India’s government agencies, researchers, and planners, to environmentalists and citizens alike.
Bhuvan was recognized by the India Economic Survey 2023-24 as a transformative application of geospatial technologies. Enabled by OGC Standards, the Bhuvan portal caters to 150,000 unique users every day, recording an impressive 20 million hits daily.
Currently, Bhuvan supports over 100 use cases and offers 150 customized solutions, including significant national initiatives such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), a rural employment scheme aimed at enhancing livelihood security; the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY), a credit-linked subsidy scheme facilitating access to affordable housing for low- and moderate-income residents; and the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), a nationwide plan to provide good all-weather road connectivity to unconnected villages.
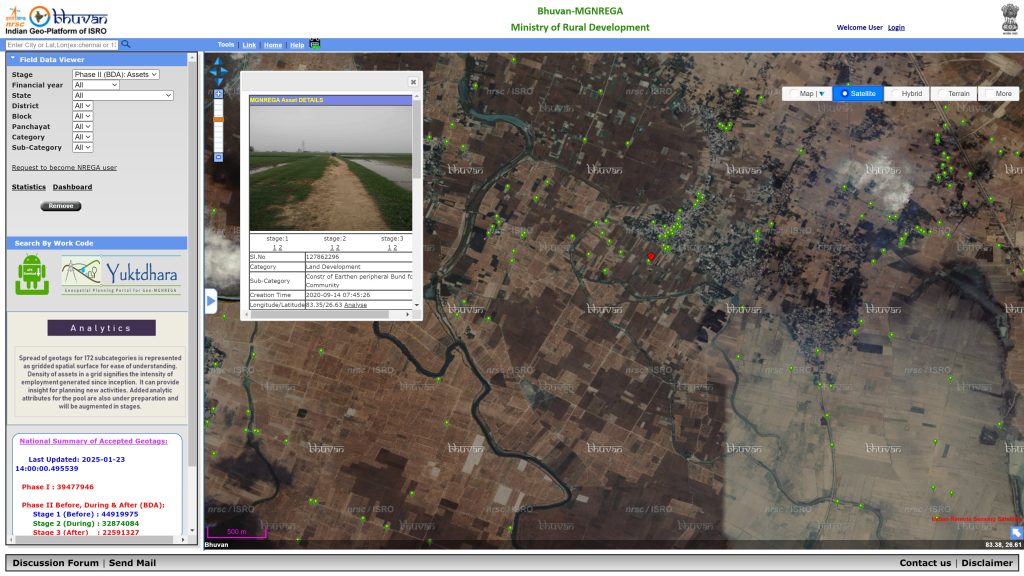
For regional developmental planning, the integration of Bhuvan with government schemes like MGNREGA has revolutionized how rural infrastructure is monitored and planned. MGNREGA focuses on creating assets such as farm ponds, check dams, irrigation canals, and sanitation facilities that support community livelihoods and generate employment for people living in rural areas. According to the Bhuvan team of NRSC, “Bhuvan initially served as an inventory tool to track these assets, ensuring a comprehensive database of the infrastructure created under the scheme. But over time, Bhuvan’s capabilities expanded to include stage-wise monitoring of asset development. This involves tracking progress before, during, and after implementation and linking it to financial disbursements. For instance, funds are released in phases based on achieving physical progress milestones, such as completing 30%, 60%, and 80% of the work. This ensures transparency and accountability in the allocation and utilization of resources.”
The platform’s advanced analytics has also helped identify zero-asset villages — areas where no MGNREGA assets had been created. This has enabled the government to address gaps in coverage, ensuring more equitable distribution of resources. For example, the reasons for the absence of agricultural activity or other socio-economic factors in these villages were analyzed to guide future planning.
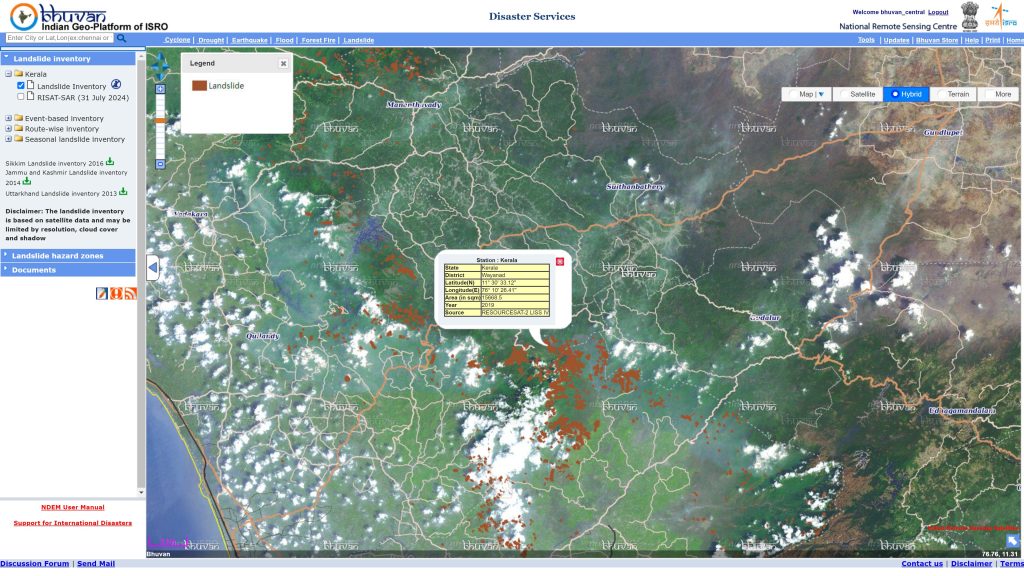
Bhuvan has proven to be an invaluable tool for disaster management as well. When cyclone Hudhud struck the east of India in 2014, the platform became a hub for real-time disaster information, as citizens uploaded over 25,000 images of cyclone-hit areas in Visakhapatnam within three days. This crowd-sourced data, combined with satellite imagery, enabled authorities to assess damage, coordinate relief, and plan recovery efforts effectively. The platform has also supported flood mapping, landslide inventories, and early warning systems, showcasing its versatility in mitigating natural disasters.
Bhuvan also played a critical role in the emergency response during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. The portal was customized to create the Bhuvan COVID-19 Dashboard, which facilitated tracking hotspots, managing food supply chains, and monitoring home isolation data. This initiative was highlighted in a UN ESCAP report on Geospatial Practices for Sustainable Development in Asia and the Pacific to showcase how technology can support public health initiatives during crises.
Bhuvan’s utility extends to urban governance as well. During the 2020 lockdown, the Telangana government employed the platform to coordinate the deployment of Mobile Rythu Bazars. Using Bhuvan’s mapping data, officials tracked and planned routes for vehicles delivering vegetables and fruits to over two million households across 3,500 locations in Hyderabad. This innovative use of GIS technology reduced market crowding while ensuring essential supplies reached residents effectively.
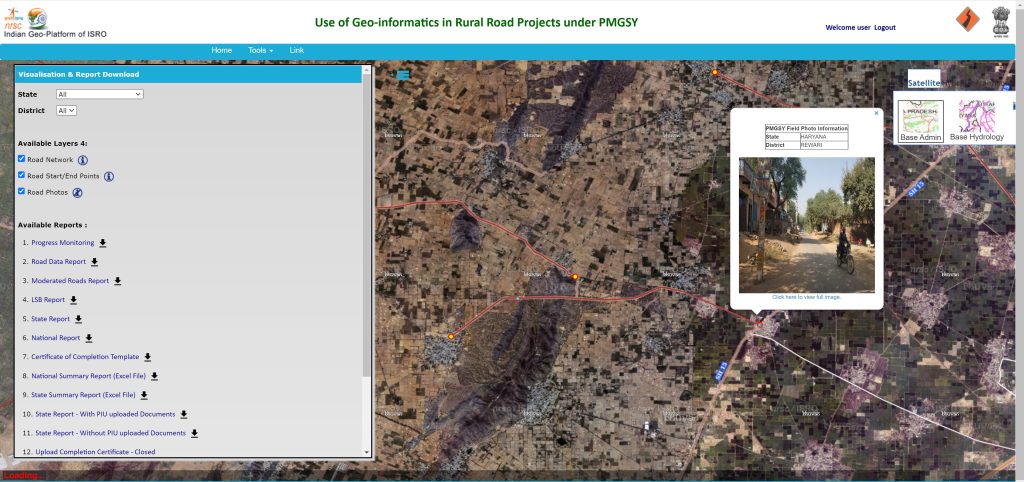
Bhuvan’s wide-ranging usefulness is further exemplified by its contributions to other sectors. The platform has been instrumental in supporting the Road Asset Management System in 2020, a flagship project by the National Highways Authority of India in collaboration with ISRO and the World Bank. By bringing public and private road networks under one umbrella, this system enhances road safety and traffic management, improves maintenance planning, and facilitates data-driven expansion of the national highway network.
Bhuvan has also contributed significantly to agricultural and environmental planning. Annual land use and land cover mapping, conducted since 2014, leverages multi-temporal satellite data to monitor agricultural activity. This data not only identifies food-secure regions but also supports applications in flood forecasting, renewable energy planning, tiger conservation, and soil erosion modelling, making it a vital resource for sustainable development. For instance, land cover data has been used to track water resources, report land degradation, and model soil erosion, offering insights for long-term resource management.
Empowering Stakeholders Through OGC Standards
The Bhuvan geoportal integrates a range of OGC Standards to facilitate seamless access, visualization, and querying of geospatial data, including:
- Web Mapping Service (WMS)
- Web Feature Service (WFS)
- Web Coverage Service (WCS)
- Catalogue Service for the Web (CSW)
- Keyhole Markup Language (KML)
- Web Map Tile Service (WMTS)
- Web Processing Service (WPS)
- Sensor Observation Service (SOS)
It supports WMS for vector and raster maps, WFS for vector data querying, WCS for raster data, CSW for metadata discovery, and open data formats like KML. Additionally, Bhuvan employs WMTS, WPS, and SOS to enhance interoperability and efficient data sharing across platforms and applications. The integration of real-time sensor data through SOS supports dynamic monitoring and analysis, making it invaluable for applications like disaster management and scenarios where timely data is critical. This comprehensive use of OGC standards boosts Bhuvan’s functionality, accessibility, and usability for different geospatial applications, as the OGC-compliant services ensure compatibility with various GIS tools, allowing users to visualize, query, and retrieve data no matter their GIS tool of choice.
“Bhuvan serves as a comprehensive repository for differing thematic databases, offering a wealth of geospatial data that supports a wide range of applications and projects across India,” according to the Bhuvan team of NRSC. “Researchers, planners, and organizations frequently rely on Bhuvan to access and download critical datasets, making it a cornerstone for informed decision-making in various sectors. Additionally, Bhuvan’s integration with Google APIs enhances its functionality, enabling seamless data access and facilitating innovative solutions for geospatial challenges. This unique combination of extensive data availability and advanced APIs underscores Bhuvan’s pivotal role in driving geospatial advancements in India.”
Building the Next Generation of Geospatial Solutions
Going forward, Bhuvan aims to enrich its offerings with updated satellite data, advanced APIs, and real-time IoT integration. Planned enhancements include citizen-focused applications relating to urban planning and dynamic data collection, as well as tailored solutions for sectors like crop insurance and tax assessment. These innovations aim to position Bhuvan as a cornerstone of geospatial data services in India, driving sustainable development and responsive, efficient, and inclusive governance across the country.